Laboratory confirmation in a reproductive failure
Sows usually abort from 3 to 21 days after the infection. Therefore, diagnostic after 21 days gets more complicated.
In some circumstances, serum from sows should not be considered as one of the first choices to diagnose reproductive failure due to PRRS virus:
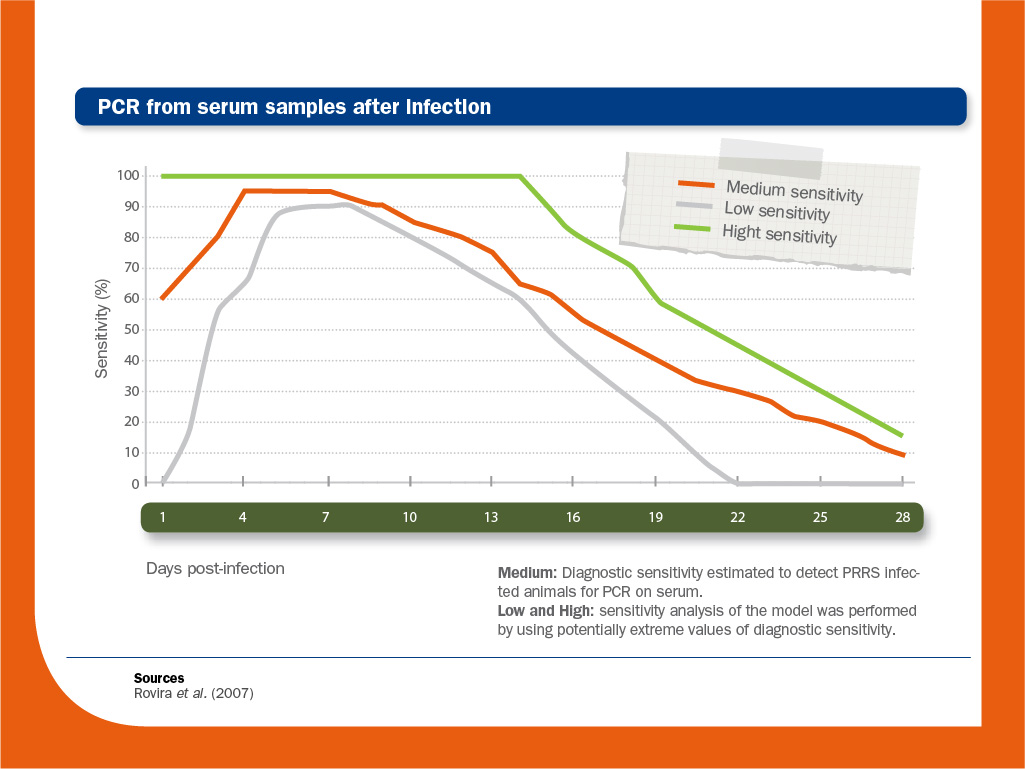
- It is difficult to detect the virus in blood by RT-PCR, since viraemia in sows is usually short (from 1 to 7 days). In front of a positive result in a recent vaccinated animal, viraemia due to vaccine virus have to be discarded using sequencing.
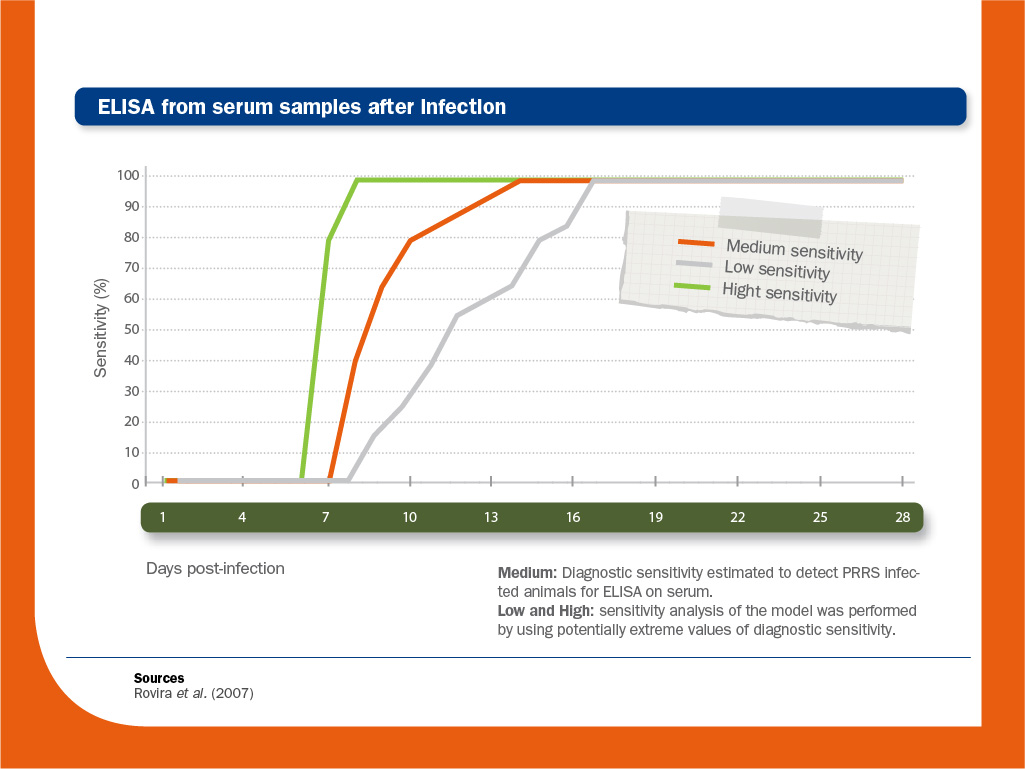
- Seroconversion by ELISA cannot be demonstrated in a previously positive or vaccinated animal/herd; seroconversion can be used to demonstrate the involvement of PRRS only when animal was previously negative.
Samples from aborted, mummified or autolysed fetuses should not be used as the main material in reproductive failure, since PRRS virus is relatively labile and rapidly disappears from these samples, that usually show negative results.
Laboratory confirmation in a respiratory outbreak
Seroconversion measured by ELISA can be used to demonstrate the involvement of PRRS virus in a respiratory outbreak.
However, seroconversion can only be observed in a previously negative animal/farm. Series of samples from various ages to detect antibodies by ELISA are useful to determine the age of the infection and, consequently, the best time to study the presence of the virus in the blood.
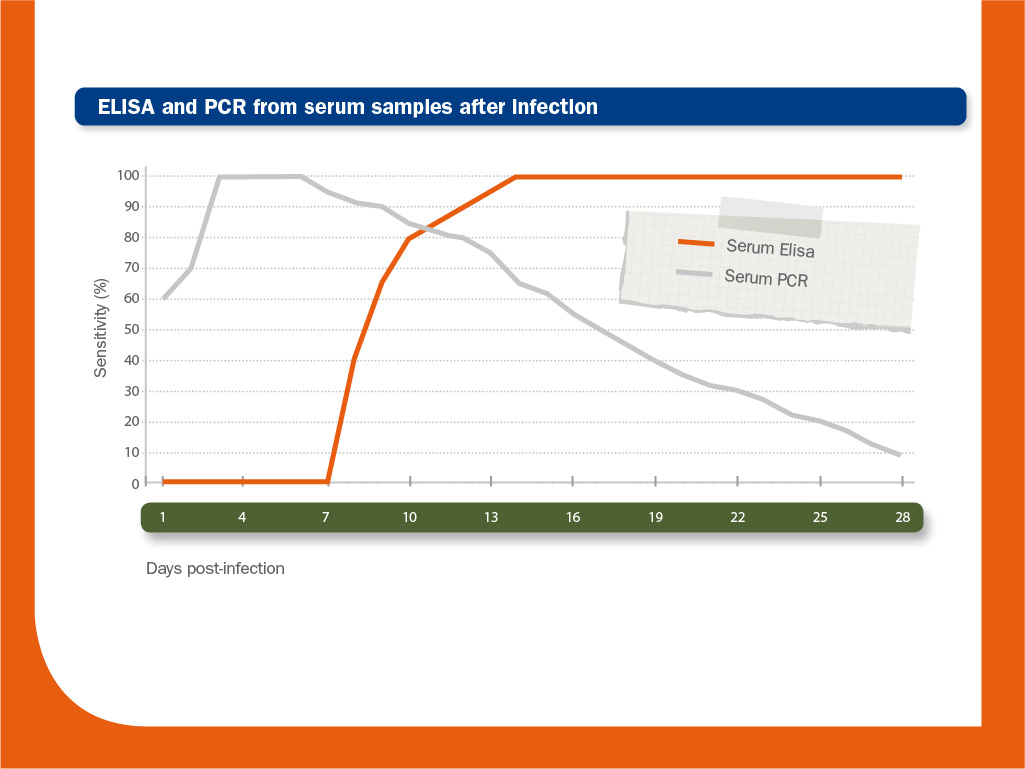
Detection of virus in sera by means of RT-PCR is useful because viraemia is longer in young pigs. Combining IHC or ISH with histopathology, the link between PRRS virus and lesions can be analysed in tissues, especially in lungs.
Combined use of ELISA and RT-PCR for PRRS diagnosis
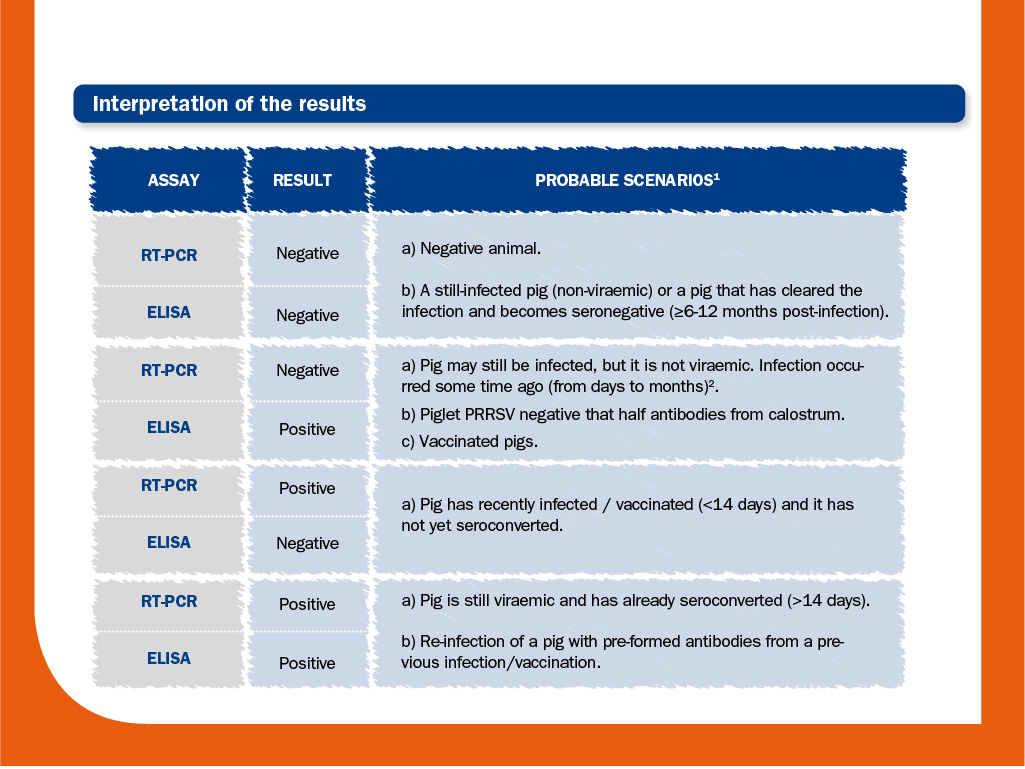
Commercial ELISAs and conventional or quantitative RT-PCR are the diagnostic tests most routinely used.
In combination, they can be used not only to detect an infection, but also to determine approximately when it occurred and to monitor the immune status at individual or at farm level.
If sequencing is also performed, we can even establish the possible sources of the virus.
1 Excluding the effects related to low sensitivity and/or low specificity.
2 In adults, viraemia is short; so, this pattern may be already observed after 14 days post-infection. In young pigs, viraemia is longer; so, this pattern may be observed after 14-28 days post-infection.
© Laboratorios Hipra, S.A. 2024. All Rights Reserved.
No part of this website or any of its contents may be reproduced, copied, modified or adapted, without the prior written consent of HIPRA.