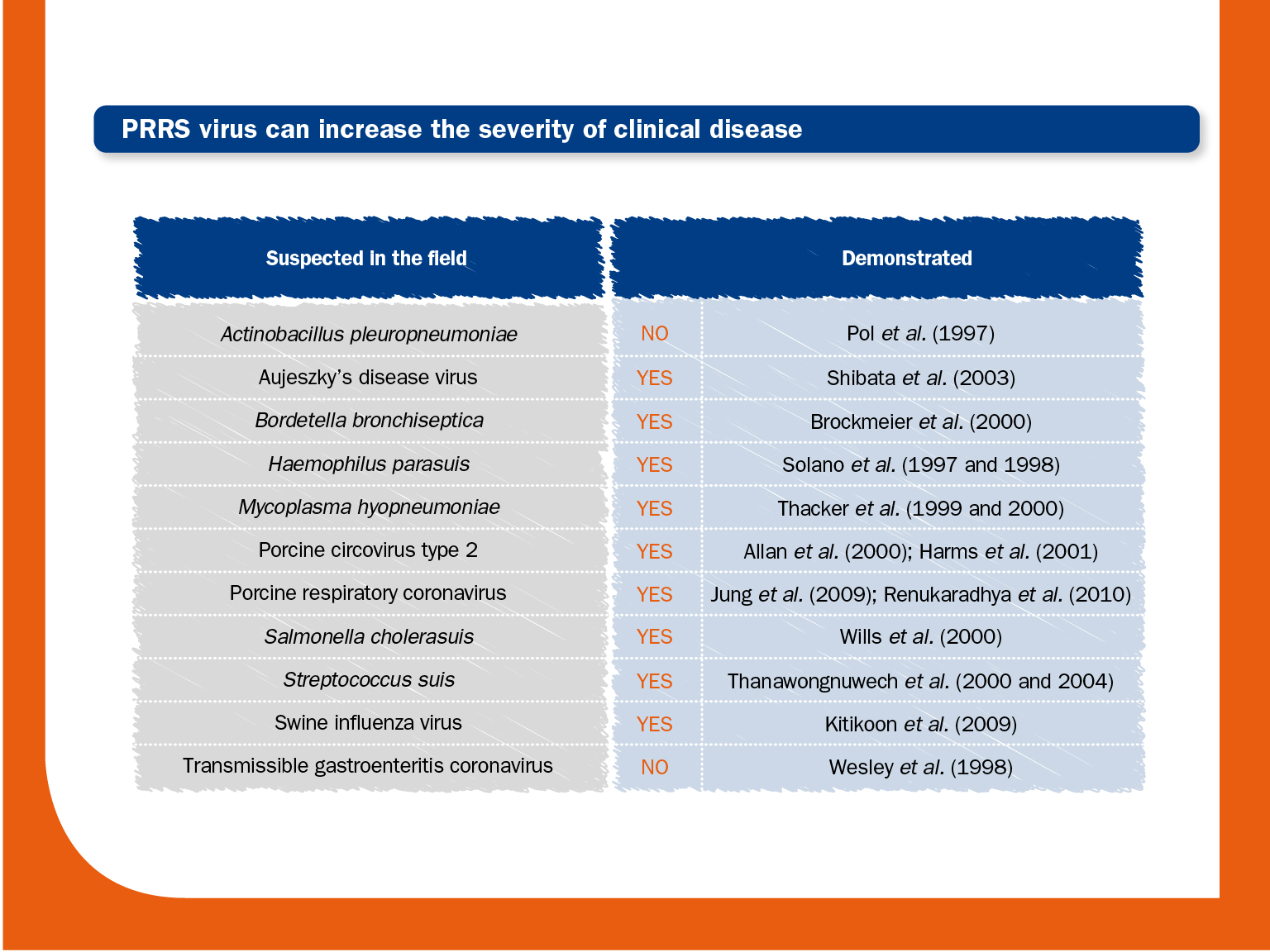
PRRS virus infection can increase the susceptibility of pigs to other infections or, alternatively, other infections may exist simultaneously with PRRS virus. Whichever the case, concurrent infections with other pathogens, whether viruses and/or bacteria, are common in most PRRS virus infections under field conditions.
Obviously, the presence of these concurrent infections complicates the clinical picture as well as the diagnosis. This phenomenon is especially noticeable in weanling and grower pigs.
Porcine respiratory disease complex (PRDC) is a term coined to define a multifactorial respiratory disorder caused by the interactions of multiple viral and bacterial pathogens, as well as management, environmental and genetic factors. It is characterized by anorexia, slow growth, fever, cough, and dyspnea.
PRRS virus infection increases the susceptibility of pigs to other infections for several reasons:
- PRRS virus damages or affects the ultrastructure of the respiratory tract; this hampers bacterial clearance.
- Alveolar macrophages, which are the main cells involved in the lungs’ defense, are the primary target cells for PRRS virus infection. More specifically, the virus replicates in the subset of alveolar macrophages with the maximal ability to phagocytize bacteria and to produce components to destroy them. Also, the virus can interact with other antigen- presenting cells.
To sum up, PRRS virus:
- … can kill infected and non-infected macrophages by inducing direct/indirect necrosis or apoptosis.
- … can decrease the bactericidal activity of macrophages.
- … can inhibit cytokines with broad antiviral properties, such as type I IFNs, even in the presence of other viruses (coinfections).
- … can induce an imbalance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines.
- … can impair the immune responses by inducing the release of certain cytokines.
- … can interfere with the correct antigen presentation.
- … can decrease cytotoxicity of NK cells.
The magnitude of the above-mentioned phenomena may vary among strains.
© Laboratorios Hipra, S.A. 2024. All Rights Reserved.
No part of this website or any of its contents may be reproduced, copied, modified or adapted, without the prior written consent of HIPRA.